Node入门系列-Express 框架的使用 — 中间件(7)
1. 什么是中间件
中间件(Middleware ),特指业务流程的中间处理环节
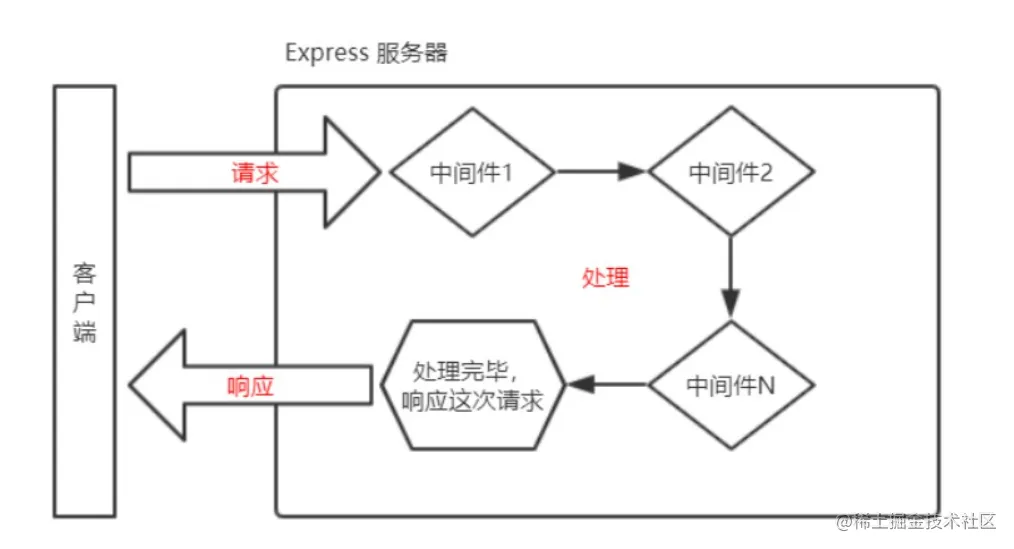
2. Express 中间件的调用流程
当一个请求到达 Express 的服务器之后,可以连续调用多个中间件,从而对这次请求进行预处理
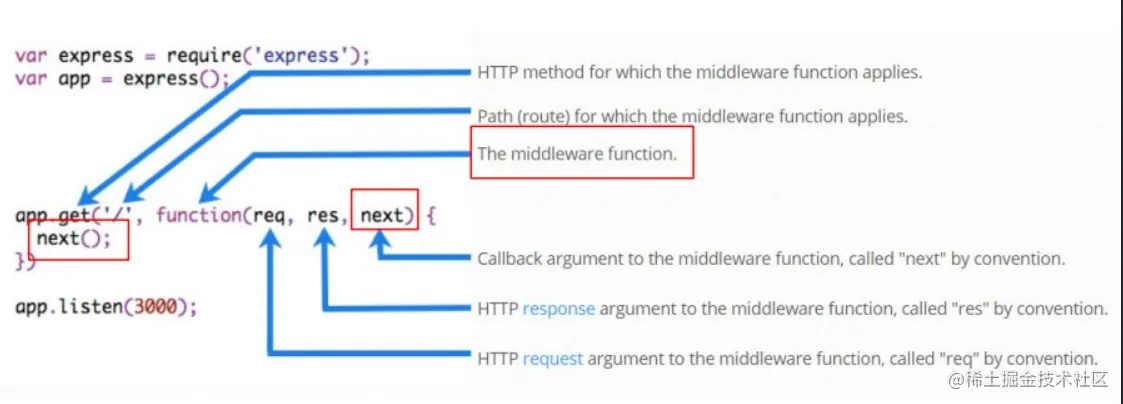
3. Express 中间件的格式
Express 的中间件,本质上就是一个 function 处理函数,Express 中间件的格式如下:
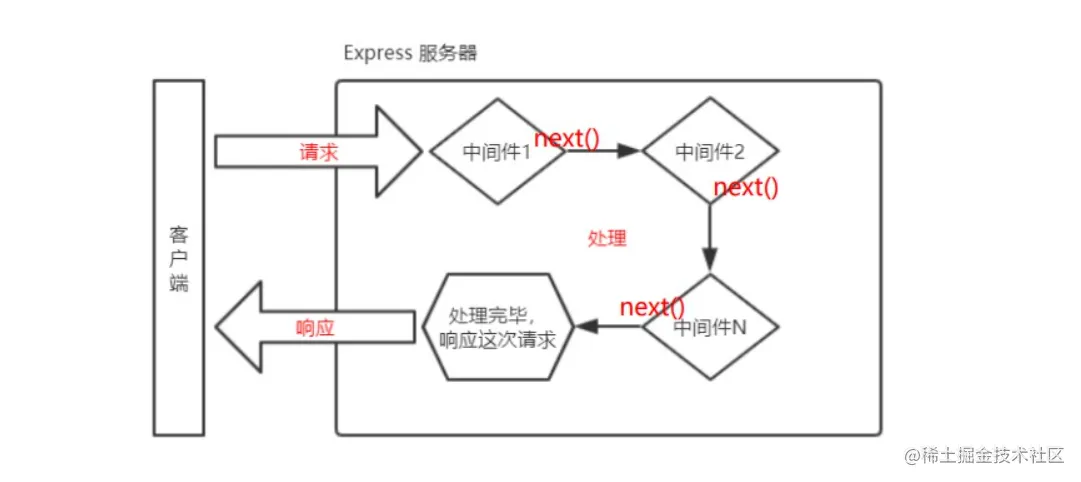
4. next 函数的作用
next 函数是实现多个中间件连续调用的关键,它表示把流转关系转交给下一个中间件或路由
5. 定义中间件函数
可以通过如下的方式,定义一个最简单的中间件函数:
// 常量 mw 所指向的,就是一个中间件函数const mw = (req, res, next) => { console.log('这是最简单的中间件函数') // 注意:在当前中间件的业务处理完毕之后,必须调用 next() 函数 // 把流转关系,转交给下一个中间件或路由 next()}6. 注册为全局生效的中间件
客户端发起的任何请求,到达服务器之后,都会触发的中间件,叫做全局生效的中间件。
通过调用 app.use(中间件函数),即可定义一个全局生效的中间件,示例代码如下:
const mw = (req, res, next) => { console.log('这是最简单的中间件函数'); // 把流转关系,转交给下一个中间件或路由 next()}
// 注册为全局生效的中间件app.use(mw)6.1 定义全局中间件的简化形式
// 定义全局中间件的简写形式app.use((req, res, next) => { console.log('这是最简单的中间件函数'); next()})7. 中间件的作用
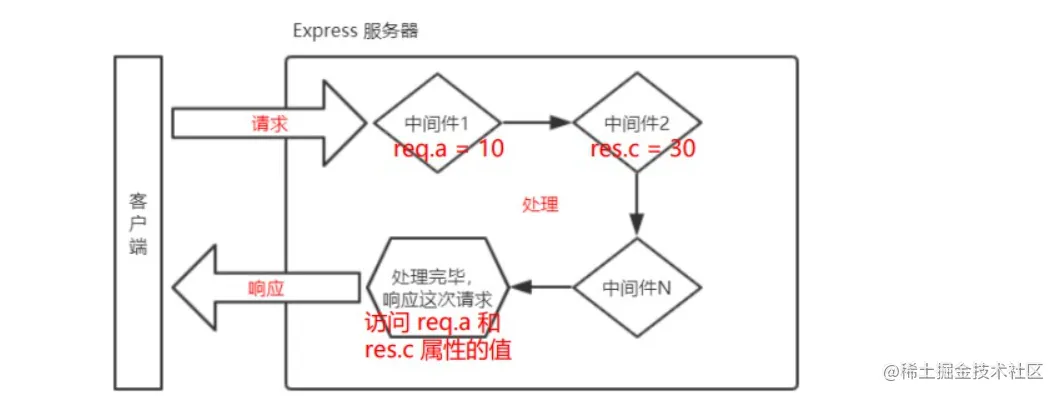
多个中间件之间,共享同一份 req 和 res。基于这样的特性,我们可以在上游的中间件中,统一为 req 或 res 对象添加自定义的属性或方法,供下游的中间件或路由进行使用。
8. 定义多个全局中间件
可以使用 app.use() 连续定义多个全局中间件。客户端请求到达服务器之后,会按照中间件定义的先后顺序依次进行调用,示例代码如下
const express = require('express')const app = express()
// 定义第一个全局中间件app.use((req, res, next) => { console.log('定义了第一个全局中间件'); next()})// 定义第二个全局中间件app.use((req, res, next) => { console.log('定义了第二个全局中间件'); next()})
// 定义路由app.get('/',(req, res) => { res.send('Home page.')})
app.listen(80, () => { console.log('server running at http://127.0.0.1');})9. 局部生效的中间件
不使用 app.use() 定义的中间件,叫做局部生效的中间件,示例代码如下
const express = require('express')const app = express()
// 定义中间件函数const mw = (req, res, next) => { console.log('定义了局部生效的中间件'); next()}
// mw 这个中间件只在 "当前路由中生效",这种用法属于 "局部生效的中间件"app.get('/', mw, (req, res) => { res.send('Home page.')})// mw 这个中间件不会影响下面这个路由 ↓↓↓app.get('/user', (req, res) => { res.send('User page.')})
app.listen(80, () => { console.log('server running at http://127.0.0.1');})10. 定义多个局部中间件
可以在路由中,通过如方式,使用多个局部中间件
// 定义中间件函数const mw1 = (req, res, next) => { console.log('调用了第一个局部生效的中间件'); next()}// 定义中间件函数const mw2 = (req, res, next) => { console.log('调用了第二个局部生效的中间件'); next()}
// mw 这个中间件只在 "当前路由中生效",这种用法属于 "局部生效的中间件"// 注意:[mw1, mw2] 这种写法也可以app.get('/', mw1, mw2, (req, res) => { res.send('Home page.')})11. 了解中间件的5个使用注意事项
-
一定要在路由之前注册中间件(除了错误级别的中间件)
-
客户端发送过来的请求,可以连续调用多个中间件进行处理
-
执行完中间件的业务代码之后,不要忘记调用 next() 函数
-
为了防止代码逻辑混乱,调用 next() 函数后不要再写额外的代码
-
连续调用多个中间件时,多个中间件之间,共享 req 和 res 对象
12. 中间件的分类
为了方便大家理解和记忆中间件的使用,Express 官方把常见的中间件用法,分成了 5 大类,分别是:
-
应用级别的中间件
-
路由级别的中间件
-
错误级别的中间件
-
Express 内置的中间件
-
第三方的中间件
12.1 应用级别的中间件
通过 app.use() 或 app.get() 或 app.post() ,绑定到app 实例上的中间件,叫做应用级别的中间件,代码示例如下
// 应用级别的中间件(全局中间件)app.use((req, res, next) => { next()})
// 应用级别的中间件(局部中间件)app.get('/', mw1, (req, res) => { res.send('Home page.')})12.2 路由级别的中间件
绑定到 express.Router() 实例上的中间件,叫做路由级别的中间件。它的用法和应用级别中间件没有任何区别。只不过,应用级别中间件是绑定到 app 实例上,路由级别中间件绑定到 router 实例上,代码示例如下:
const express = require('express')const app = express()const router = express.Router()
// 路由级别的中间件router.use((req, res, next) => { console.log('Time', Date.now()) next()})
app.use('/', router)12.3 错误级别的中间
错误级别中间件的作用:专门用来捕获整个项目中发生的异常错误,从而防止项目异常崩溃的问题。
格式:错误级别中间件的 function 处理函数中,必须有 4 个形参,形参顺序从前到后,分别是 (err, req, res, next)。
const express = require('express')const app = express()
// 1. 定义路由app.get('/', (req, res) => { // 1.1 人为制造错误 throw new Error('服务器内部发生了错误!')})
// 2. 定义错误级别的中间件,捕获整个项目的异常错误,从而防止程序崩溃app.use((err, req, res, next) => { console.log('发生了错误!' + err.message); res.send('Error: ' + err.message)})
app.listen(80, () => { console.log('server running at http://127.0.0.1');})注意:错误级别的中间件,必须注册在所有路由之后!
12.4 Express内置的中间件
自 Express 4.16.0 版本开始,Express 内置了 3 个常用的中间件,极大的提高了 Express 项目的开发效率和体验:
-
express.static 快速托管静态资源的内置中间件,例如: HTML 文件、图片、CSS 样式等(无兼容性)
-
express.json 解析 JSON 格式的请求体数据(有兼容性,仅在 4.16.0+ 版本中可用)
-
express.urlencoded 解析 URL-encoded 格式的请求体数据(有兼容性,仅在 4.16.0+ 版本中可用)
12.4.1 演示 express.json 解析 JSON 格式的请求体数据
const express = require('express')const app = express()
// 注意:除了错误级别的中间件,其他中间件,必须在路由之前配置// 通过 express.json() 这个中间件,解析表单中的 JSON 格式的数据app.use(express.json())
//todo 演示 express.json 解析 JSON 格式的请求体数据 ↓↓↓app.post('/user', (req, res) => { // 在服务器,可以使用 req.body 这个属性,来接收客户端发送过来的请求体数据 // 默认情况下,如果不配置解析表单数据的中间件,则 req.body 默认等于 undefined console.log(req.body); res.send('ok')})
app.listen(80, () => { console.log('express server running at http://127.0.0.1');})12.4.2 演示 express.urlencoded 解析 URL-encoded 格式的请求体数据
const express = require('express')const app = express()
// 通过 express.urlencoded() 这个中间件,解析表单中的 url-encoded 格式的数据app.use(express.urlencoded({exrended: false}))
//todo 演示 express.urlencoded 解析 URL-encoded 格式的请求体数据 ↓↓↓app.post('/book', (req, res) => { // 在服务器端,可以通过 req.body 来获取 JSON 格式的表单数据和 url-encoded 格式 console.log(req.body); res.send('ok')})
app.listen(80, () => { console.log('express server running at http://127.0.0.1');})12.5 第三方的中间件
非 Express 官方内置的,而是由第三方开发出来的中间件,叫做第三方中间件。在项目中,大家可以按需下载并配置 第三方中间件,从而提高项目的开发效率。
例如:在 [email protected] 之前的版本中,经常使用 body-parser 这个第三方中间件,来解析请求体数据。使用步 骤如下:
- 运行
npm install body-parser安装中间件 - 使用
require导入中间件 - 调用
app.use()注册并使用中间件
const express = require('express')const app = express()
// 1. 导入解析表单数据的中间件 body-parserconst parser = require('body-parser')// 2. 使用 app.use() 注册中间件app.use(parser.urlencoded({extended: false}))
app.post('/user', (req, res) => { console.log(req.body) res.send('ok')})
app.listen(80, () => { console.log('express server running at http://127.0.0.1');})注意:Express 内置的 express.urlencoded 中间件,就是基于 body-parser 这个第三方中间件进一步封装出来的。
每文一句:少年读书,如隙中窥月;中年读书,如庭中望月;老年读书,如台上玩月。皆以阅历之深浅,为所得之深浅耳。