全面拥抱Vue3,Vuex4 最新详解教程!
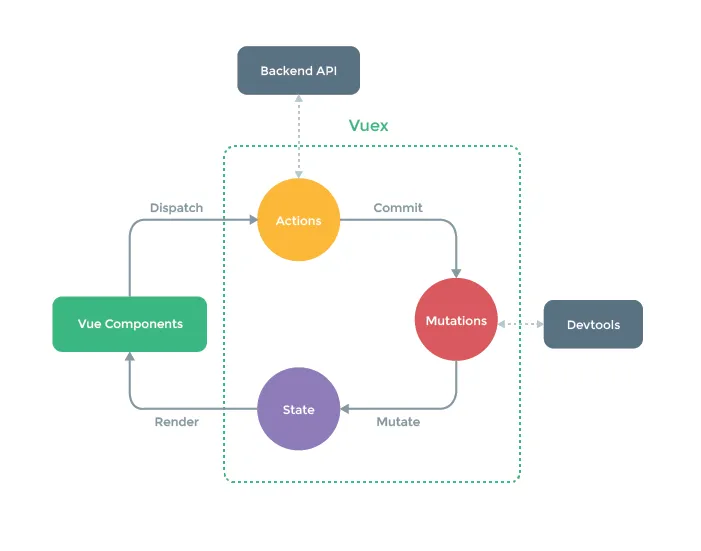
Vuex4 的工作流程
1. 学习初始
这里使用 vuecli 来快速创建一个vue3项目,这里选择 JS 编写(使用 JS 或 TS 都可以)
vue create learn_vux2. 安装
我们这里使用的是vuex4.x,安装的时候需要添加 next 指定版本
npm install vuex@next --save3. 基本配置
3.1 创建仓库
在 src 目录下创建 store/index.js store 仓库
import { createStore } from "vuex";
const store = createStore({
})
export default store3.2 在 main.js 文件中,有以下两个步骤:
import { createApp } from 'vue'import App from './App.vue'
// 1. 导入 storeimport store from './store'
// 2. 挂载到 Vue 根实例createApp(App).use(store).mount('#app')这样,一个 Vuex 仓库就构建完成啦!
4. state 选项的使用 state
全局共享的数据,只允许在 mutation 中修改(后面会讲)
state提供唯一的公共数据源,所有共享的数据都要统一放到Store的state中进行存储state必须写成函数的形式并在return的对象中存放数据
import { createStore } from "vuex";
const store = createStore({ // state 提供唯一的公共数据源 state() { return { count: 10 } }})export default store4.1 在组件中的 template 和 script 中使用 state
- 在 setup 中,必须通过实例
useStore()才能拿到store中的数据 - 通过
compute获取store数据(缺点是数据只能一条一条取)
<template> <!-- 获取state --> <h2>{{ $store.state.count }}</h2> <h2>{{ ucount }}</h2></template>
<script>import { computed } from 'vue'import { useStore } from 'vuex'export default { name: 'App', setup() { // 实例 useStore(),获取 store 对象 const store = useStore() // // 通过 compute 获取 store 数据 const ucount = computed(() => store.state.count);
return { ucount, } }}</script>5. mapState 辅助函数
- 在组件中的 script 中使用
mapState,options API(Vue2) 的写法:
<template> <div> <h2>Home:{{ $store.state.counter }}</h2> <h2>Home:{{ sCounter }}</h2> <h2>Home:{{ sName }}</h2> </div></template><script>// 使用 mapState 辅助函数import { mapState } from 'vuex'export default { // 也可以使用展开运算符和来原有的computed混合在一起; computed: { // 1. 数组写法 // ...mapState(["counter", "name", "age", "height"])
// 2. 对象写法(可以给state里面的值换个变量名) ...mapState({ sCounter: state => state.counter, sName: state => state.name }) }}</script>- 在组件中的 script 中使用
mapState,composition API(Vue3) 的写法:
<template> <div> <h2>{{counter}}</h2> <h2>{{name}}</h2> <h2>{{age}}</h2> <h2>{{height}}</h2> <hr> </div></template>
<script>import { mapState, useStore } from 'vuex'import { computed } from 'vue'
export default { setup() { // 开始获取数据 const storeStateFns = mapState(["counter", "name", "age", "height"]) // {name: function, age: function, height: function} // 转化为: // {name: ref, age: ref, height: ref} const storeState = {} // 1. 取出 storeStateFns 中所有的 key,并遍历 Object.keys(storeStateFns).forEach(fnKey => { // 2. 通过调用函数身上的 bind() 方法去绑定this,也就是store(属性为$store,值为store) const fn = storeStateFns[fnKey].bind({$store: store}) // 3. 将 fn 函数转化为compute的形式赋值给每一个对应的key(其实就是store中state的变量,而函数则是每一个对应的值) storeState[fnKey] = computed(fn) })
return { ...storeState } }}</script>setup 中使用 mapState 会比较麻烦一点,现在来对这个方法进行封装:
在 src 目录下,创建 hook/useState.js 文件
import { computed } from 'vue'import { mapState, useStore } from 'vuex'
export function useState(mapper) { // 拿到store对象 const store = useStore()
// 获取到对应的对象的functions: {name: function, age: function} const storeStateFns = mapState(mapper)
// 对数据进行转换 const storeState = {} Object.keys(storeStateFns).forEach(fnKey => { const fn = storeStateFns[fnKey].bind({$store: store}) storeState[fnKey] = computed(fn) })
return storeState}在组件中的 script 使用方式如下:
import { useState } from '../hooks/useState'
export default { setup() { // 数组、对象的写法都支持 const storeState = useState(["counter", "name", "age", "height"]) const storeState2 = useState({ sCounter: state => state.counter, sName: state => state.name })
return { ...storeState, ...storeState2 } }}6. getters 选项的使用 getters
getters 可以对 Store 中已有的数据加工处理之后形成新的数据,类似 Vue 的计算属性。注意:getters 中只能返回用于展示的数据,不可修改数据
import { createStore } from "vuex";
const store = createStore({ state() { return { count: 10 } }, // Store 中数据发生变化,getters 的数据也会跟着变化。 // 参数一:state,可以获取到 state 里面的数据 // 参数二:getters,可以使用其他 getters 的值 getters: { doubleCount(state, getters) { return state.count * 2 } // doubleCount:state => { // return state.count * 2 // } }})export default store注意:可以采用箭头函数的写法、state 为上面的数据源、必须 return 出值
6.1 在组件中的 template 和 script 中使用 getters
<template> <!-- 获取getters --> <h2>doubleCount: {{ $store.getters.doubleCount}}</h2> <h2>doubleCount: {{dcount}}</h2></template>
<script>import { computed } from 'vue';import { useStore, mapState } from 'vuex'export default { name: 'App', setup() { const store = useStore() // 获取getters const dcount = store.getters.doubleCount // 结合 computed 使用 // const dcount = computed(() => store.getters.doubleCount)
return { dcount } }}</script>6.2 getters 的返回值可以是个函数
getters 的返回值是一个函数,可以接收参数,然后调用这个函数。一般用于需要接收参数的时候使用
import { createStore } from "vuex";
const store = createStore({ state() { return { count: 10 } }, getters: { countN(state, getters) { // 调用时接收一个参数 return function(n) { return state.count + n } } }})export default storetemplate 中使用时就要调用这个 return 的函数
<template> <h2>countN: {{$store.getters.countN(5)}}</h2></template>7. mapGetters 辅助函数
- 在组件中的 script 中使用
mapGetters,options API 的写法:
<template> <div> <h2>{{ ageInfo }}</h2> <h2>{{ heightInfo }}</h2> <h2>{{ sNameInfo }}</h2> <h2>{{ sAgeInfo }}</h2> </div></template>
<script> import { mapGetters } from 'vuex' export default { // option API 写法 computed: { // 数组写法 ...mapGetters(["nameInfo", "ageInfo", "heightInfo"]), // 对象写法 ...mapGetters({ sNameInfo: "nameInfo", sAgeInfo: "ageInfo" }) }, }</script>- 在组件中的 script 中使用
mapGetters,composition API 的写法:
- setup 中使用 mapGetters 跟使用 mapState 的方法差不多,这里也先封装成一个hook,然后直接调用。 在 src 目录下,创建 hook/useGetters.js 文件
import { computed } from 'vue'import { mapGetters, useStore } from 'vuex'
export function useGetters(mapper) { // 拿到store对象 const store = useStore()
// 获取到对应的对象的functions: {name: function, age: function} const storeStateFns = mapGetters(mapper)
// 对数据进行转换 const storeState = {} Object.keys(storeStateFns).forEach(fnKey => { const fn = storeStateFns[fnKey].bind({$store: store}) storeState[fnKey] = computed(fn) })
return storeState}在组件中的使用方式如下:
<template> <div> <h2>传统写法:{{ sNameInfo }}</h2> <h2>{{ nameInfo }}</h2> <h2>{{ ageInfo }}</h2> <h2>{{ heightInfo }}</h2> <hr> </div></template>
<script>import { computed } from 'vue'import { useStore } from 'vuex'import { useGetters } from '../hooks/useGetters'
export default { setup() { // 传统写法 const store = useStore(); const sNameInfo = computed(() => store.getters.nameInfo);
// 封装 getters 后的写法 const storeGetters = useGetters(["nameInfo", "ageInfo", "heightInfo"])
return { sNameInfo, ...storeGetters } }}</script>8. mutations 选项的使用 mutations
一条重要的原则就是要记住 mutation 必须是同步函数
- Mutation 用于变更 Store中 的数据。
- 只能通过 mutation 变更 Store 数据,不可以直接操作 Store 中的数据。
- 通过这种方式虽然操作起来稍微繁琐一些,但是可以集中监控所有数据的变化。
import { createStore } from "vuex";
const store = createStore({ state() { return { count: 10 } }, getters: { doubleCount(state, getters) { return state.count * 2 } },
// 参数一:state,可以获取state中的数据 // 参数二:载荷,即额外的参数 // 在大多数情况下,载荷应该是一个对象,这样可以包含多个字段并且记录的 mutation 会更易读 mutations: { increment(state, payload) { state.count += payload.num } }})export default store8.1 在组件中的 template 和 script 中提交 mutations
<template> <div> <hr> <button @click="$store.commit('increment')">+1</button> <button @click="addTen">+10</button> <hr> </div></template>
<script>export default { methods: { addTen() { // 普通的写法 // this.$store.commit('incrementN', {num: 10})
// 另外一种提交风格 this.$store.commit({ type: 'increment_n', num: 10, }) } }}</script>9. mapMutations 辅助函数
<template> <div> <h2>当前计数: {{ $store.state.counter }}</h2> <hr> <button @click="increment">+1</button> <button @click="add">+1</button> <hr> </div></template>
<script>import { mapMutations, mapState } from 'vuex'
export default { // options API 中的使用 methods: { ...mapMutations(["increment", ]), ...mapMutations({ add: "increment" }) },
// composition API 中的使用 setup() { const storeMutations = mapMutations(["increment",])
return { ...storeMutations } }}</script>10. actions 选项的使用 actions
Action 类似于 mutation,不同在于:
- Action 提交的是 mutation,而不是直接变更状态。
- Action 可以包含任意异步操作。
import { createStore } from "vuex";
const store = createStore({ state() { return { count: 10 } }, getters: { doubleCount(state, getters) { return state.count * 2 } }, mutations: { increment(state, payload) { state.count ++ } }, // 1. actions 用于处理异步任务 // 2. 在 actions 中,不能直接修改 state 中的数据 // 3. 必须通过 context.commit() 触发某个 mutations 才行 actions: { incrementAction(context, payload) { console.log(payload) setTimeout(() => { context.commit('increment') }, 1000); }, }})export default store10.1 组件中使用,派发 actions
<template> <div> <button @click="increment">+1</button> <button @click="add">+1</button> <hr> </div></template>
<script>import { useStore, mapState } from 'vuex'
export default { // composition API 的写法 setup() { const store = useStore() const add = () => { store.dispatch('incrementAction', {count: 100}) } }
// options API 的写法 methods: { increment() { // 携带参数 this.$store.dispatch("incrementAction", {count: 100}) }, decrement() { // 3.派发风格(对象类型) this.$store.dispatch({ type: "decrementAction" }) } }}</script>11. mapActions 辅助函数
<template> <div> <h2>当前计数: {{ $store.state.counter }}</h2> <hr> <button @click="incrementAction">+1</button> <button @click="decrementAction">-1</button> <button @click="add">+1</button> <button @click="sub">-1</button> <hr> </div></template>
<script>import { mapActions } from 'vuex'
export default { // options API 写法 methods: { // ...mapActions(["incrementAction", "decrementAction"]), // ...mapActions({ // add: "incrementAction", // sub: "decrementAction" // }) },
// composition API 写法 setup() { const actions = mapActions(["incrementAction", "decrementAction"]) const actions2 = mapActions({ add: "incrementAction", sub: "decrementAction" })
return { ...actions, ...actions2 } }}</script>12. modules 选项的使用 modules
Vuex 允许我们将 store 分割成模块(module)。每个模块拥有自己的 state、mutation、action、getter、甚至是嵌套子模块——从上至下进行同样方式的分割。
由于modules 内容太多且稍显复杂,这里不在演示,若想继续学习可前往官网学习
每文一句:非学无以广才,非志无以成学。
ok,关于 Vuex4 的简单使用就到这里,看到这里相信你对 Vuex4 已经有了简单的了解。如果想对 Vuex4 进行更加深入的理解,请移步 Vuex4中文文档 深入研究。